2023/3/20
【最新情報:論文掲載完了】
Morishita R, Shimada M, Nagao M, Shimizu S, Kamei N, Takeda-Morishita M. In Vivo Proof of Biological Safety and Physiological Effects of Orally Ingested Water Containing H2-Filled Ultrafine Bubbles (UFBs). Biol Pharm Bull. 2023;46(2):343-347.
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/bpb/46/2/46_b22-00631/_article
【要旨】
シンバイオシス株式会社が特許を取得した製造方法で製造される、ナノサイズの微細気泡(ナノバブル/ウルトラファインバブル)を含む水素NanoGAS®️水は、腸内フローラ移植臨床研究会にて糞便微生物叢移植の溶媒に活用されている。このナノサイズの微細気泡はその微細さから水中での長期安定性を有することが知られている。水素は抗酸化効果を持つが、水に溶けにくい性質を持つことから、これらを組み合わせた水素ナノバブル水の飲水は、水素の効果的な摂取を可能とする可能性がある。一般的にナノバブルは生体に対し毒性や障害性を持たないと考えられているが、長期間の飲水における安全性は検討されていなかった。
そこで今回は、マウスを用いて、水素NanoGAS®️水の1、3ヶ月の亜慢性期間における飲水試験を行い、血液生化学検査及び消化・代謝臓器における病理組織学検査において安全性を評価した。
結果、水素NanoGAS®️水を3ヶ月間飲水してもNanoGAS®️による障害性は認められず、水素NanoGAS®️水の飲水は生体に対し毒性を示さず、水素NanoGAS®️水は体に優しい素材であることが明らかとなった。
【目的】
NanoGAS®️の長期飲水安全性を検証する。
【検証方法】
無処置雄性ddYマウスにH2 NanoGAS®️ 水、ミネラルウォーター(MW: Natural Mineral water)、NanoGAS®️の原料水であるRO waterをそれぞれ1ヶ月及び3ヶ月飲水させ、飼育最終日に血液検査及び病理組織学検査を行なった。また、週次摂餌量・飲水量・体重を測定し、3ヶ月飼育群は週次血糖値を測定した。1ヶ月飼育群は試験初日及び最終日のみ血糖値測定を行った。
【結果】
Table 1 Blood biochemical parameters following 1and 3 months oral intake of NM water, RO water or NanoGAS® water

血液検査において、水の種類間におけるパラメータ変動は確認されず、障害性は認められなかった。有意差なし。
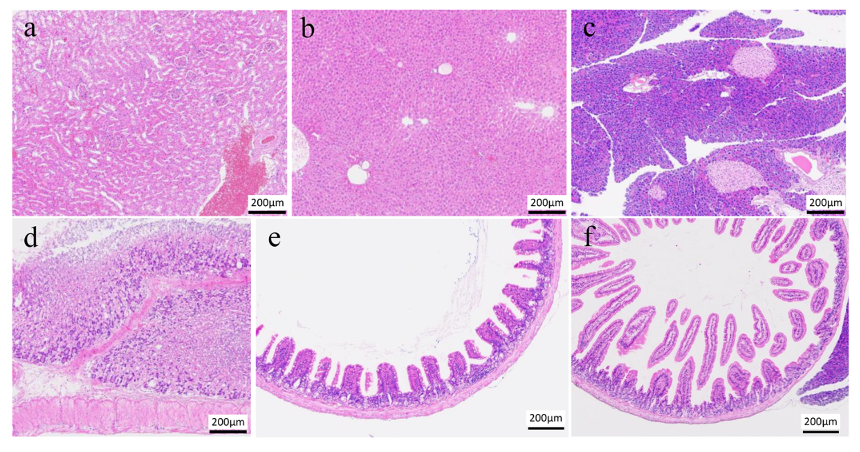
Fig. 1. Photomicrographs of the Organ Tissue and Mucosal Membranes of a Representative Mouse in the NanoGAS® Water Group Following 3 Months Intake
(a) Left Kidney, (b) Liver, (c) Pancreas, (d) Stomach, (e) Small intestine (Jejunum) and (f) Small Intestine (Ileum). The bar indicates 200 µm. Tissues were stained with hematoxylin and eosin after fixation in 10% formalin neutral buffer solution.
Fig.1は、3ヶ月H2 NanoGAS®️水を飲水したマウスの代謝・消化系臓器の病理組織学検査の結果である。臓器像においても、NanoGAS®️水の飲水に起因する障害は見られなかった。
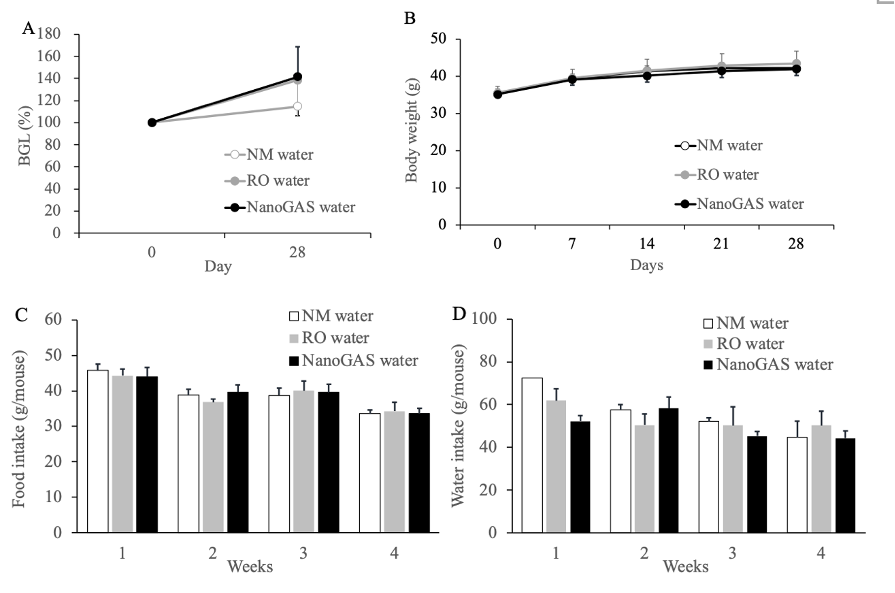
Figure 2 Effect of 1 month intake of NM water, RO water, or NanoGAS® water on BGLs, Body weight, amount of food intake, and amount of drinking water in normal ddY mice. (A) BGLs, (B) Body weight, (C) Food intake, and (D) Water intake. Data indicate the mean ± S.E.M values (N=3-4). Data of drinking water of NM water on week 1 was N=2.
1ヶ月飼育群の血糖値・体重・摂餌量・飲水量の推移。群間で大きく異なる点はなかった。有意差なし。
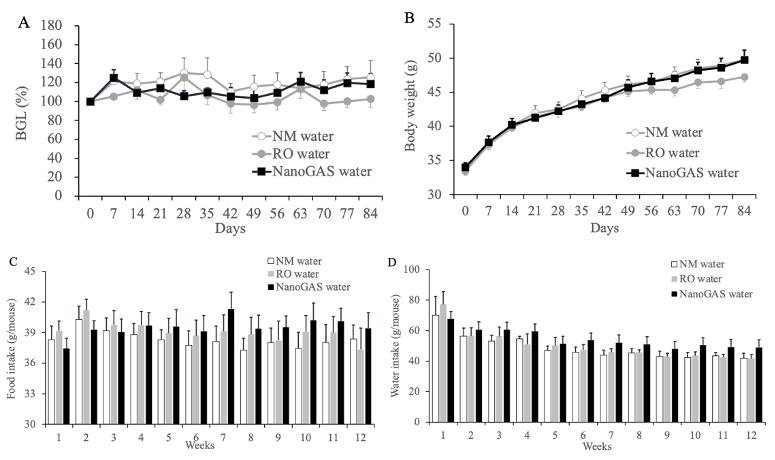
Figure 3 Effect of 3 months intake of NM water, RO water, or NanoGAS® water on BGLs, Body weight, amount of food intake, and amount of drinking water in normal ddY mice. (A) BGLs, (B) Body weight, (C) Food intake (N=6-7), and (D) Water intake (N=3-7). Data indicate the mean ± S.E.M values.
3ヶ月飼育群の血糖値・体重・摂餌量・飲水量の推移。群間で大きく異なる点はなく、有意差も見られなかった。観察期間後半の摂餌量において、NanoGAS群でいくらか高い摂餌量飲水量が確認されたが、体重の推移はNW群と同じ推移を示したので、NanoGASが栄養吸収効率に効果を示したのかもしれない。
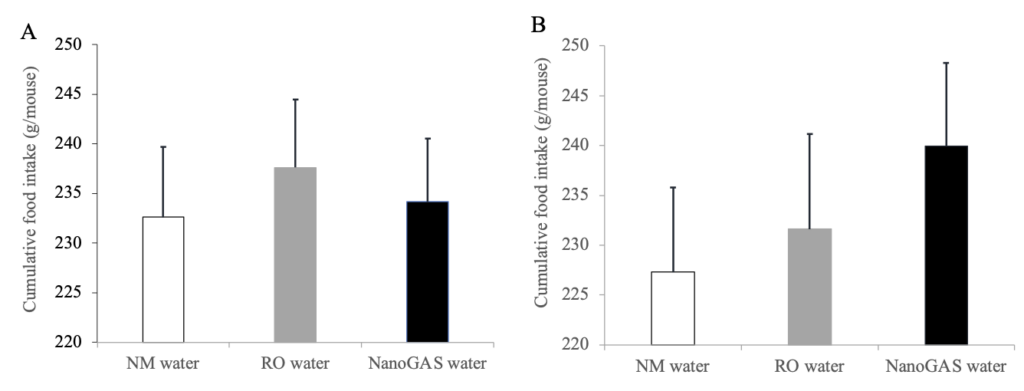
Figure 4 Effect of 3 months intake of NM water, RO water, or NanoGAS® water on cumulative food intake in normal ddY mice. (A) Cumulative food intake in the first half of study period (Weeks 1-6) and (B) Cumulative food intake in the latter half of study period (Weeks 7-12). Data indicate the mean ± S.E.M values (N=6-7).
3ヶ月飼育群の飼育前半・後半の摂餌量の比較。Fig.3でも記述した飼育後半期のNanoGAS群の摂餌量の増加傾向が見られたが、有意差はなかった。
また、酸素においては成長促進効果が見られているが(Ebina K, et al., PLoS One, (2013))、水素は成長促進ではなく代謝亢進作用が知られており、食物摂取量の増加に関係する可能性がある。しかし、水素が成長を促進したという直接的な報告はないため、水素を充填したUFB水の潜在的な生物学的効果を推定するためには、詳細な研究が必要である。