Original Research Article: “Suspension Sterilization Effect of NanoGAS” was published.
Mar. 18, 2023
Morishita R, Itoh S, Takeda-Morishita M. Evaluation of Bactericidal Effects of H2- and O3-filled Ultrafine Bubbles Water. Biocontrol Sci. 2022;27(3):139-142.
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/bio/27/3/27_139/_article/-char/ja
Background and Purpose
It has been shown that microbubbles have a bactericidal effect, but the relationship between the bactericidal effect and the gas species enclosed in the microbubbles has not yet been clarified.
In particular, the sterilizing effect of microbubbles containing hydrogen, which has an antioxidant effect, has not been confirmed.
Therefore, we have conducted a bacterial suspension test to investigate the bactericidal effect of hydrogen-filled NanoGAS water ( H2 NanoGAS water) and ozone-filled NanoGAS water (O3 NanoGAS water), both of which have bactericidal effects, and observed changes over time in the bacterial survival rate.
[Verification method]
The following four types of test water were used.
H2NanoGAS®︎ water
– O3NanoGAS®︎ water
– Water for injection (IW)
– Saline
0.1 mL of each of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) andEscherichia coli (E. coli ) bacteria solution adjusted to a concentration of 1000 CFU/mL each was suspended in 0.9 mL of each test water. Immediately after suspension, the suspension was applied to two sheets (0.1 mL/sheet) of flat plate medium. After 1, 3, 6, and 9 hours of suspension, the same suspension was applied to two sheets of plate medium. All plate media were incubated at 37°C. Bacterial counts were performed at 24 hours for E.coli and 48 hours for S.aureus, and bacterial survival rates were calculated using the following formula.
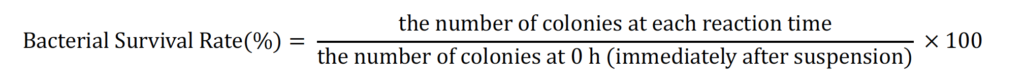
Result

図1 E.coliの細菌生存率の経時的変化(*:IWと比較してp<0.05の割合で有意差あり。N.D.:検出不可)
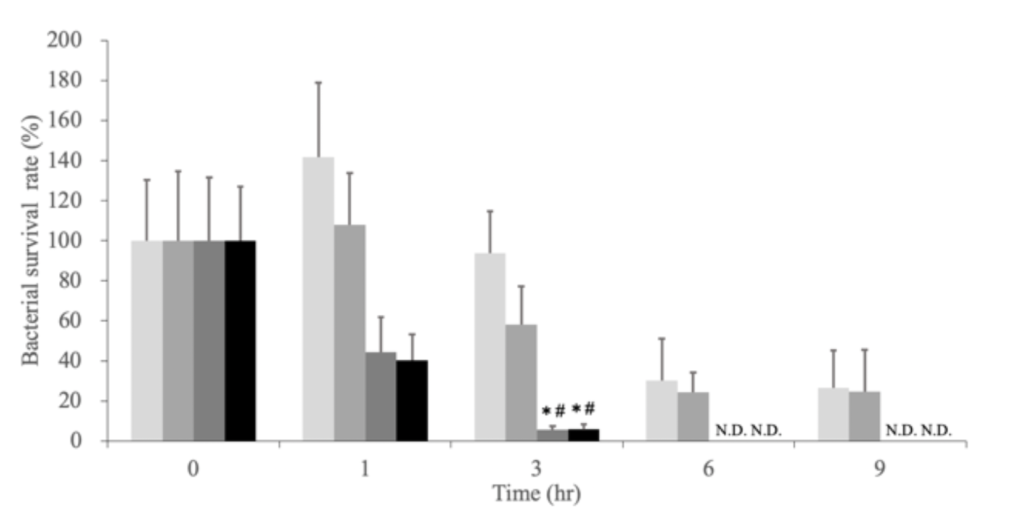
図2 S. aureusの細菌生存率の経時的変化(#: Salineと比較してp<0.01の割合で有意差あり, *:IWと比較してp<0.05の割合で有意差あり N.D.:検出不可)
Regardless of the enclosed gas, in both H2 andO3NanoGAS®️ groups, E.coli showed significantly lower bacterial survival at 6 hours compared to IW, and S.aureus showed significantly lower bacterial survival at 3 hours compared to IW and Saline.
Compared to other research reports (Yamaguchi et al., 2021), the NanoGAS®️ water used in this study had fewer Nanobubble particles and took longer to show bactericidal effect. These results suggest that in the bacterial suspension method, the bactericidal power may depend on the number of Nanobubble.
FURTHER RESEARCH IS NEEDED ON THE RELATIONSHIP OF CRUSH, ENCLOSED GASES, AND ROS (REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES) GENERATION TO STERILIZATION.